Glioblastoma Brain Cancer: Understanding, Treatment, and Hope for the Future
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a devastating and aggressive form of brain cancer. Characterized by its rapid growth and infiltration into surrounding brain tissue, it presents significant challenges for diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the complexities of GBM, providing a detailed understanding of its nature, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and ongoing research efforts that offer a glimmer of hope for the future.
Understanding Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma is a type of glial cell tumor, meaning it originates from glial cells, which support and protect neurons. It is classified as a grade IV astrocytoma, the highest grade on the grading scale for brain tumors. This grade reflects its rapid growth rate and poor prognosis. GBM tumors are highly invasive, meaning they send out finger-like projections into the surrounding brain tissue, making complete surgical removal incredibly difficult, if not impossible.
Symptoms of Glioblastoma
Symptoms of glioblastoma can vary widely depending on the location and size of the tumor. They can develop gradually or appear suddenly. Common symptoms include:
- Headaches, often worsening over time
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness in a limb
- Vision problems
- Speech difficulties
- Personality changes
- Memory problems
- Nausea and vomiting
- Balance problems
It’s crucial to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions. If you experience any of these, particularly if they are persistent or worsening, seeking medical attention promptly is essential.
Diagnosis of Glioblastoma
Diagnosing glioblastoma involves a multi-step process. It typically begins with a neurological examination and medical history review. Imaging tests are crucial, including:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of the brain, allowing for visualization of the tumor’s size, location, and extent.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Provides cross-sectional images of the brain, which can help to identify the tumor.
A biopsy is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This involves surgically removing a small sample of the tumor tissue for microscopic examination by a pathologist. The biopsy helps determine the grade of the tumor and plan the most effective treatment strategy.
Treatment Options for Glioblastoma
Treatment for glioblastoma is typically multi-modal, meaning it combines several approaches to maximize effectiveness. These approaches include:
1. Surgery
Surgical resection aims to remove as much of the tumor as safely possible. However, due to the invasive nature of GBM, complete removal is often not achievable. The extent of surgical resection depends on the tumor’s location and the patient’s overall health.
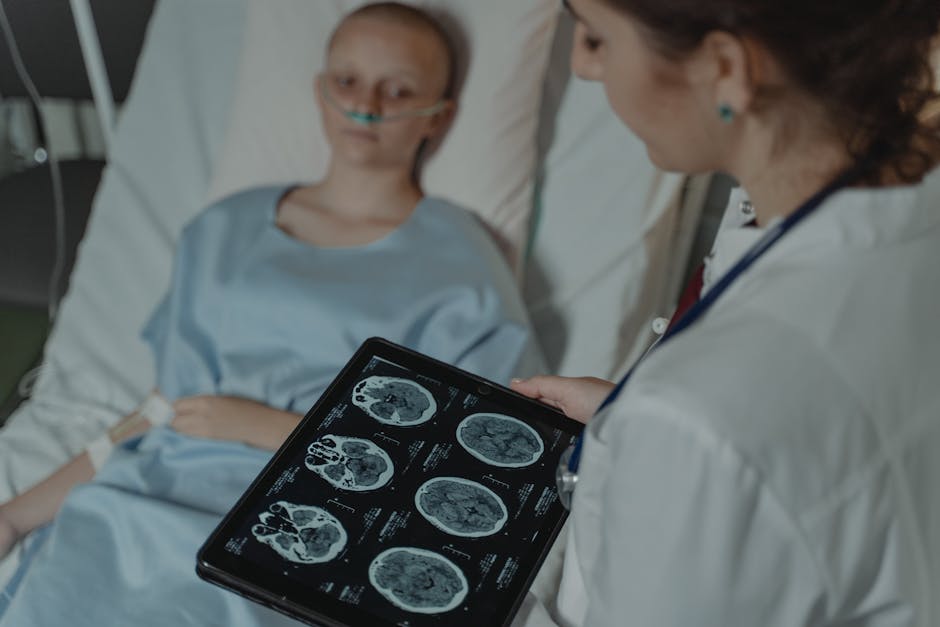
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It’s often used after surgery to target any remaining tumor cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. External beam radiation therapy is the most common type used for GBM.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Temozolomide is a common chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of GBM, often administered both before and after surgery and radiation.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are designed to specifically target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Research continues to explore new targeted therapies for GBM.
5. Clinical Trials
Participation in clinical trials offers access to innovative treatments and therapies that are not yet widely available. These trials play a critical role in advancing GBM research and improving treatment outcomes.
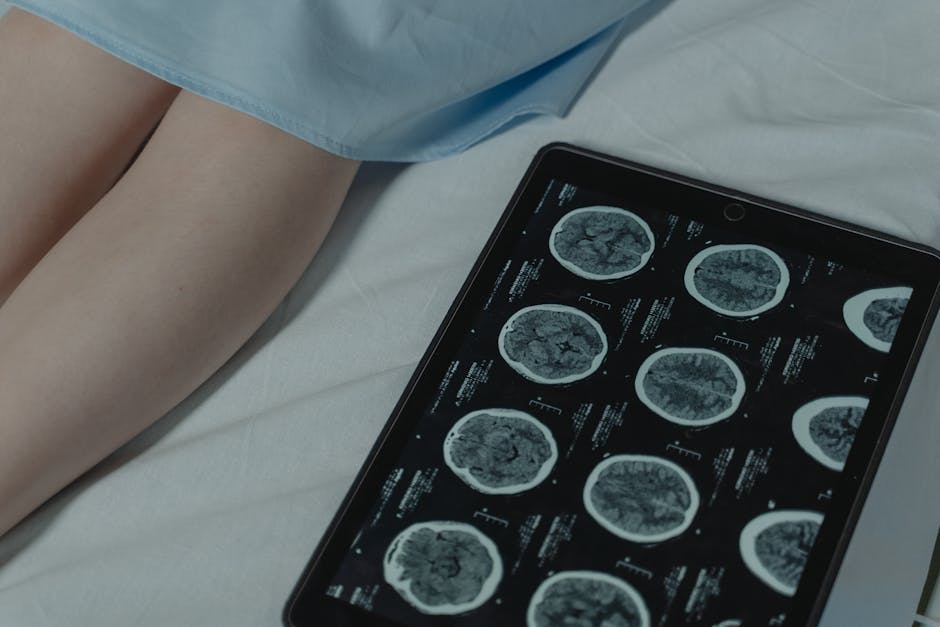
Research and Future Hope
Despite the challenges posed by glioblastoma, significant advancements are being made in research. Scientists are actively exploring various avenues, including:
- Immunotherapy: Harnessing the power of the immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Gene therapy: Modifying genes to target cancer cells.
- Oncolytic viruses: Using viruses to selectively infect and destroy cancer cells.
- Nanomedicine: Developing nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to tumor cells.
These advancements offer hope for improved treatment outcomes and potentially even a cure for glioblastoma in the future.
Support and Resources
Living with glioblastoma can be incredibly challenging for patients and their families. Several organizations offer support and resources, including:
- The National Brain Tumor Society
- The American Brain Tumor Association
- The National Cancer Institute
These organizations provide information about GBM, support groups, and financial assistance programs. They offer a vital lifeline for individuals and families navigating the complexities of this disease.
Glioblastoma is a formidable opponent, but ongoing research, advancements in treatment, and the unwavering support of medical professionals and patient advocacy groups offer a path towards a brighter future. Early detection and prompt treatment remain crucial in improving prognosis and quality of life for those affected by this aggressive cancer.